Kubernetes的授权是基于插件形式的,其常用的授权插件有以下几种:
Node(节点认证)
ABAC(基于属性的访问控制)
RBAC(基于角色的访问控制)
Webhook(基于http回调机制的访问控制)
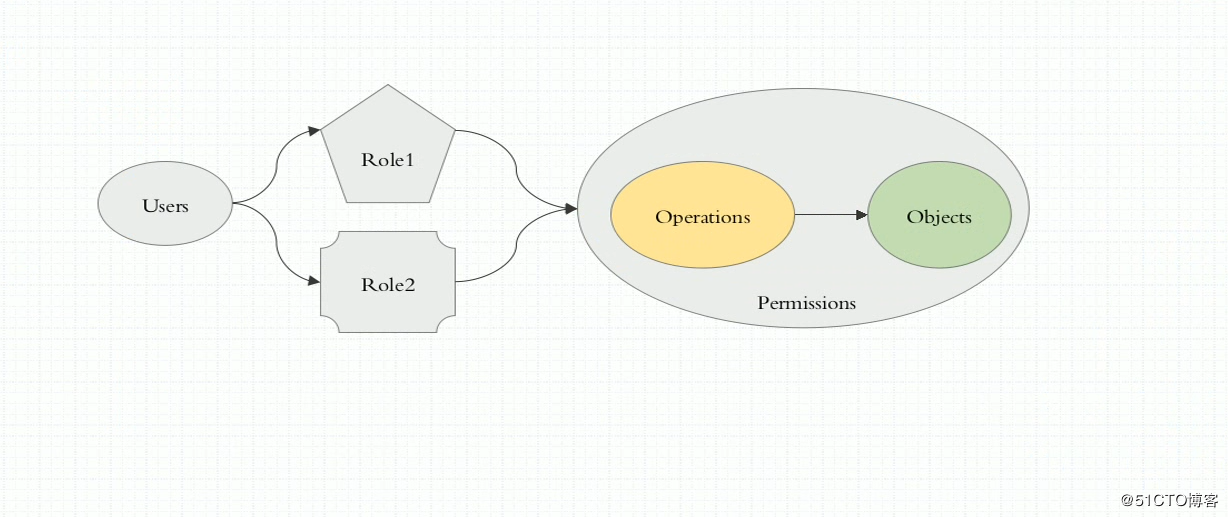
让一个用户(Users)扮演一个角色(Role),角色拥有权限,从而让用户拥有这样的权限,随后在授权机制当中,只需要将权限授予某个角色,此时用户将获取对应角色的权限,从而实现角色的访问控制。如图:
基于角色的访问控制(Role-Based Access Control, 即”RBAC”)使用”rbac.authorization.k8s.io” API Group实现授权决策,允许管理员通过Kubernetes API动态配置策略。
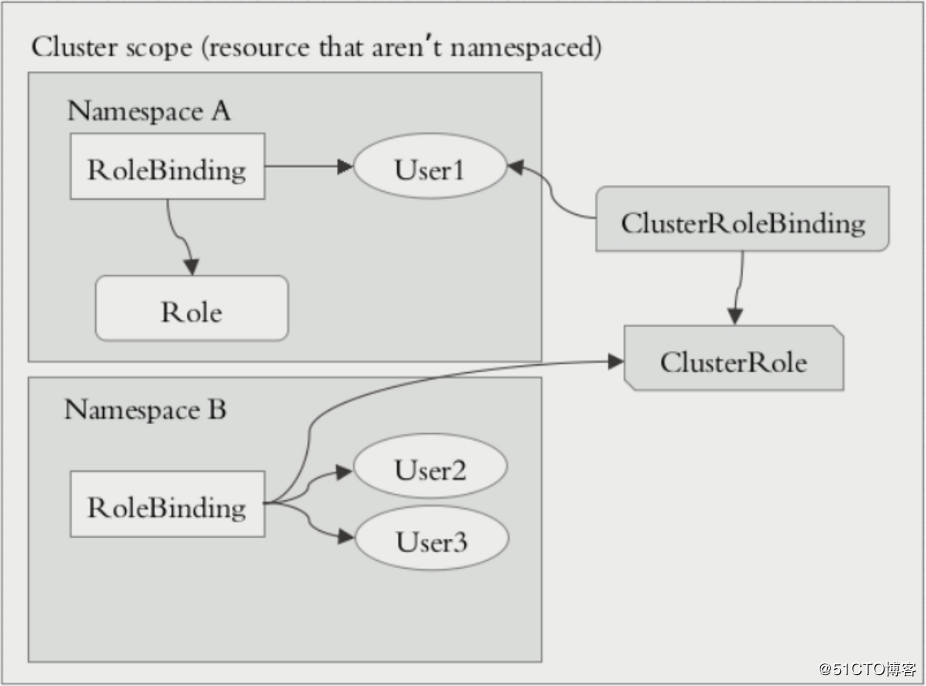
在k8s的授权机制当中,采用RBAC的方式进行授权,其工作逻辑是把对对象的操作权限定义到一个角色当中,再将用户绑定到该角色,从而使用户得到对应角色的权限。此种方式仅作用于名称空间当中,这是什么意思呢?当User1绑定到Role角色当中,User1就获取了对该NamespaceA的操作权限,但是对NamespaceB是没有权限进行操作的,如get,list等操作。
另外,k8s为此还有一种集群级别的授权机制,就是定义一个集群角色(ClusterRole),对集群内的所有资源都有可操作的权限,从而将User2,User3通过ClusterRoleBinding到ClusterRole,从而使User2、User3拥有集群的操作权限。
这里有2种绑定ClusterRoleBinding、RoleBinding。但是也可以使用RoleBinding去绑定ClusterRole。
当使用这种方式进行绑定时,用户仅能获取当前名称空间的所有权限。为什么这么绕呢??举例有10个名称空间,每个名称空间都需要一个管理员,而该管理员的权限都是一致的。那么此时需要去定义这样的管理员,使用RoleBinding就需要创建10个Role,这样显得更加繁重。为此当使用RoleBinding去绑定一个ClusterRole时,该User仅仅拥有对当前名称空间的集群操作权限,换句话说,此时只需要创建一个ClusterRole就解决了以上的需求。(注意:RoleBinding仅仅对当前名称空间有对应的权限)
在RBAC API中,一个角色就是一组权限的集合, 权限以纯粹的累加形式累积(没有”否定”的规则)。 角色由命名空间(namespace)内的Role对象定义,而整个Kubernetes集群范围内有效的角色则通过ClusterRole对象实现。
角色(Role) 角色只能对命名空间内的资源进行授权,以下示例描述了”default”命名空间中定义了一个Role对象,用于授予对pod的读访问权限:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 kind: RoleapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1metadata: namespace: default name: pod-readerrules: "" ] # "" 空字符串,表示核心 API 群 resources: ["pods" ] verbs: ["get" , "watch" , "list" ]
rules 中的参数说明如下
apiGroups:支持的 API 组列表,例如apiVersion: batch/v1、 apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1、 apiVersion: apps/v1beta1 等。
resource:支持的资源对象列表,例如 pods、deployments、jobs 等。
verbs:对资源对象的操作方法列表,例如 get, list, watch, create, update, patch, delete,deletecollection 。
集群角色(Cluster Role) 集群角色除了具有和角色一致的名称空间内资源的管理能力,因其集群级别的范围,还可以用于以下特殊元素的授权。
集群范围的资源(例如 Node(节点))
非资源型的路径(例如 /healthz)
包含全部名称空间的资源,例如 pods(用于 kubectl get pods --all-namespaces 这样的操作授权)。
下面的集群角色可以让用户有权访问任意一个或所有命名空间的 secrets(取决于其绑定方式):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 kind: ClusterRoleapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1metadata: # 鉴于ClusterRole是作用于整个集群范围对象,所以这里不需要定义"namespace" 字段 name: secret-readerrules: "" ] resources: ["secrets" ] verbs: ["get" , "watch" , "list" ]
RoleBinding与ClusterRoleBinding 角色绑定(Role Binding)将一个角色中定义的各种权限授予一个或者一组用户。 角色绑定包含了一组相关主体(即subject, 包括用户——User、用户组——Group、或者服务账户——Service Account)以及对被授予角色的引用。 在命名空间中可以通过RoleBinding对象授予权限,而集群范围的权限授予则通过ClusterRoleBinding对象完成。
RoleBinding可以引用在同一命名空间内定义的Role对象。 下面示例中定义的RoleBinding对象在”default”命名空间中将”pod-reader”角色授予用户”jane”。 这一授权将允许用户”jane”从”default”命名空间中读取pod。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 # 以下角色绑定定义将允许用户"jane" 从"default" 命名空间中读取pod。 kind: RoleBindingapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1metadata: name: read-pods namespace: defaultsubjects: # 赋予用户jane pod-reader角色权限 name: jane apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.ioroleRef: kind: Role # 此字段必须是 Role 或 ClusterRole name: pod-reader # 此字段必须与你要绑定的 Role 或 ClusterRole 的名称匹配,也就是说此 Role 或 ClusterRole必须存在 apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
RoleBinding对象也可以引用一个ClusterRole对象用于在RoleBinding所在的命名空间内授予用户对所引用的ClusterRole中 定义的命名空间资源的访问权限。这一点允许管理员在整个集群范围内首先定义一组通用的角色,然后再在不同的命名空间中复用这些角色。(这样做的目的是创建一个通用权限的ClusterRole,如果需要创建10个名称空间管理员的时候只需要用RoleBinding和ClusterRole绑定即可,不用创建10个role和10个RoleBinding,只需要一个ClusterRole和十个RoleBinding就搞定了)
例如,尽管下面示例中的RoleBinding引用的是一个ClusterRole对象,但是用户”dave”(即角色绑定主体)还是只能读取”development” 命名空间中的secret(即RoleBinding所在的命名空间)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 # 以下角色绑定允许用户"dave" 读取"development" 命名空间中的secret。 kind: RoleBindingapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1metadata: name: read-secrets namespace: development # 这里表明仅授权读取"development" 命名空间中的资源。 subjects: name: dave apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.ioroleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: secret-reader # 引用上面定义的clusterRole 名称(clusterRole没有指定命名空间,默认可以应用所有,但是在rolebinding时,指定了命名空间,所以只能读取本命名空间的文件) apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
最后,可以使用ClusterRoleBinding在集群级别的所有名称空间中授予权限。下面示例中所定义的ClusterRoleBinding 允许在用户组”manager”中的任何用户都可以读取集群中任何名称空间中的secret。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 # 以下`ClusterRoleBinding`对象允许在用户组"manager" 中的任何用户都可以读取集群中任何命名空间中的secret。 kind: ClusterRoleBindingapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1metadata: name: read-secrets-globalsubjects: name: manager apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.ioroleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: secret-reader apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
对资源的引用 大多数资源由代表其名字的字符串表示,例如”pods”,就像它们出现在相关API endpoint的URL中一样。然而,有一些Kubernetes API还 包含了”子资源”,比如pod的logs。在Kubernetes中,pod logs endpoint的URL格式为:
1 GET /api/ v1/namespaces/ {namespace}/pods/ {name}/log
在这种情况下,”pods”是命名空间资源,而”log”是pods的子资源。为了在RBAC角色中表示出这一点,我们需要使用斜线来划分资源 与子资源。如果需要角色绑定主体读取pods以及pod log,您需要定义以下角色:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 kind: RoleapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1metadata: namespace: default name: pod-and-pod-logs-readerrules: "" ] resources: ["pods" , "pods/log" ] # 根据上面意思表示授予读取pods和pods下log的权限 verbs: ["get" , "list" ]
角色定义的例子 以下示例均为从 Role 或 ClusterRole 对象中截取出来,我们仅展示其 rules 部分
允许读取core API Group中定义的资源”pods”:
1 2 3 4 rules: "" ] resources: ["pods" ] verbs: ["get" , "list" , "watch" ]
允许读写在”extensions”和”apps” API Group中定义的”deployments”:
1 2 3 4 rules: "extensions" , "apps" ] resources: ["deployments" ] verbs: ["get" , "list" , "watch" , "create" , "update" , "patch" , "delete" ]
允许读取”pods”以及读写”jobs”:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 rules:"" ]"pods" ]"get" , "list" , "watch" ]"batch" , "extensions" ]"jobs" ]"get" , "list" , "watch" , "create" , "update" , "patch" , "delete" ]
允许读取一个名为”my-config”的ConfigMap实例(需要将其通过RoleBinding绑定从而限制针对某一个命名空间中定义的一个ConfigMap实例的访问):
1 2 3 4 5 rules: "" ] resources: ["configmaps" ] resourceNames: ["my-config" ] verbs: ["get" ]
允许读取core API Group中的”nodes”资源(由于Node是集群级别资源,所以此ClusterRole定义需要与一个ClusterRoleBinding绑定才能有效):
1 2 3 4 rules: "" ] resources: ["nodes" ] verbs: ["get" , "list" , "watch" ]
允许针对非资源端点 “/healthz” 及其所有子路径的”GET”和”POST”请求(此ClusterRole定义需要与一个ClusterRoleBinding绑定才能有效):
1 2 3 rules: "/healthz" , "/healthz/*" ] # 在非资源URL中,'*' 代表后缀通配符 verbs: ["get" , "post" ]
对角色绑定主体(Subject)的引用 RoleBinding或者ClusterRoleBinding将角色绑定到角色绑定主体(Subject)。 角色绑定主体(kind指定)可以是用户组(Group)、用户(User)或者服务账户(Service Accounts)。
用户由字符串表示。可以是纯粹的用户名,例如”alice”、电子邮件风格的名字,如 “bob@example.com ” 或者是用字符串表示的数字id。由Kubernetes管理员配置认证模块 以产生所需格式的用户名。对于用户名,RBAC授权系统不要求任何特定的格式。然而,前缀system:是 为Kubernetes系统使用而保留的,所以管理员应该确保用户名不会意外地包含这个前缀。
Kubernetes中的用户组信息由授权模块提供。用户组与用户一样由字符串表示。Kubernetes对用户组 字符串没有格式要求,但前缀system:同样是被系统保留的。
服务账户(serviceAccount)拥有包含 system:serviceaccount:前缀的用户名,并属于拥有system:serviceaccounts:前缀的用户组。
说明:
system:serviceaccount: (单数)是用于服务账户用户名的前缀;
system:serviceaccounts: (复数)是用于服务账户组名的前缀。
角色绑定例子 以下示例中,仅截取展示了RoleBinding的subjects字段。
一个名为”alice@example.com ”的用户:
1 2 3 4 subjects:User name : "alice@example.com"
一个名为”frontend-admins”的用户组:
1 2 3 4 subjects:Group name : "frontend-admins"
kube-system命名空间中的默认服务账户:
1 2 3 4 subjects : - kind: ServiceAccount name : default namespace : kube-system
对于任何名称空间中的 “qa” 组中所有的服务账户:
1 2 3 4 subjects : - kind: Group name : system:serviceaccounts:qa apiGroup : rbac.authorization.k8s.io
对于 “development” 名称空间中 “dev” 组中的所有服务帐户:
1 2 3 4 5 subjects : - kind: Group name : system:serviceaccounts:dev apiGroup : rbac.authorization.k8s.io namespace : development
在集群中的所有服务账户:
1 2 3 4 subjects : - kind: Group name : system:serviceaccounts apiGroup : rbac.authorization.k8s.io
所有认证过的用户:
1 2 3 4 subjects : - kind: Group name : system:authenticated apiGroup : rbac.authorization.k8s.io
所有未认证的用户:
1 2 3 4 subjects : - kind: Group name : system:unauthenticated apiGroup : rbac.authorization.k8s.io
所有用户:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 subjects : - kind: Group name : system:authenticated apiGroup : rbac.authorization.k8s.io - kind: Group name : system:unauthenticated apiGroup : rbac.authorization.k8s.io
重点注意 在创建Rolebinding 或是Clusterrolebinding时如果是ServiceAccount则需指定Namespace字段
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 [root@master-1 pki ]apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: RoleBinding metadata: creationTimestamp: null name: heihei roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: Role name: pods-reader subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: admin namespace: kube-system
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 [root@master-1 pki]Name: leader-locking-nfs-provisioner Labels: <none> Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: "apiVersion" :"rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1" ,"kind" :"RoleBinding" ,"metadata" :{"annotations" :{},"name" :"leader-locking-nfs-provisioner" ,"na... Role: Kind: Role Name: leader-locking-nfs-provisioner Subjects: Kind Name Namespace ---- ---- --------- ServiceAccount nfs-provisioner default
在创建Rolebinding 或是Clusterrolebinding如果是User、Group时无需指定Namespace字段
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 [root@k8s-master-01 ~ ]Name: ye-read-pods Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Role: Kind: ClusterRole Name: pods-reader Subjects: Kind Name Namespace ---- ---- --------- User k8s-user-test
创建User Account访问Kubernetes集群 此步骤在/etc/kubernetes/pki路径下执行,因为需要用到Kubernetes CA证书
生成证书 1 2 3 4 5 [root@k8s-master-01 pki ]# (umask 077;openssl genrsa -out k8s-user-test.key 2048) private key, 2048 bit long modulusis 65537 (0x10001 )
1 2 [root@k8s-master-01 pki] 1 root root 1675 12月 16 17:02 k8s-user-test.key
使用ca.crt进行签署 1 [root@k8s - master-01 pki]# openssl req - new - key k8s- user - test.key - out k8s- user - test.csr - subj "/CN=k8s-user-test" # 证书签署请求(CN表示用户名,O表示组)
1 2 3 4 [root@k8s-master-01 pki]# openssl x509 -req -in k8s-user-test .csr -CA ./ca .crt -CAkey ./ca .key -CAcreateserial -out k8s-user-test .crt -days 1000 #证书签署test CA Private Key
1 [root@k8s -master-01 pki]# openssl x509 -in k8s-user-test.crt -text -noout
role定义(User –> Rolebinding –> Role) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 [root@k8s-master-01 pki ]apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: Role metadata: creationTimestamp: null name: pods-reader rules: - apiGroups: - "" resources: - pods verbs: - get - list - watch
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 [root@k8s-master-01 pki]# kubectl create role pods-reader --verb=get,list,watch --resource=pods --dry-run=client -o yaml > role-demo.yaml [root@k8s-master-01 pki]# vim role-demo.yaml apiVersion : rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind : Role metadata : creationTimestamp : null name : pods-reader rules : - apiGroups: - "" resources : - pods verbs : - get - list - watch
1 2 [root@k8s-master-01 pki]# kubectl apply -f role -demo.yaml #角色创建role .rbac.authorization .k8s.io/pods-reader created
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 [root@k8s - master-01 pki]# kubectl get role- reader 3 s@k8s - master-01 pki]# kubectl describe role pods- reader- reader< none > < none > - Resource URLs Resource Names Verbsget list watch] #此处已经定义了pods- reader这个角色对pods资源拥有get 、list、watch的权限
rolebinding定义 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 [root@k8s-master-01 pki ]root@k8s-master-01 pki ]apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: RoleBinding metadata: creationTimestamp: null name: ye-read-pods roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: Role name: pods-reader subjects: - apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: User name: k8s-user-test
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 [root@k8s-master -01 pki]read -pods createdmaster -01 pki]read -pods<none> <none> Role Name : pods-readerUser k8s-user-test
添加用户认证 1 2 [root@k8s-master-01 pki]# kubectl config set-credentials k8s-user-test --client-certificate =./k8s-user-test.crt --client-key =./k8s-user-test.key --embed-certs =true User "k8s-user-test" set.
1 2 [root@k8s-master-01 pki]# kubectl config set-context k8s-user-test@kubernetes --cluster =kubernetes --user =k8s-user-test"k8s-user-test@kubernetes" created.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 [root@k8s-master-01 pki ]apiVersion: v1 clusters: - cluster: certificate-authority-data: DATA+OMITTED server: https://172.16.50.200:6443 name: kubernetes contexts: - context: cluster: kubernetes user: k8s-user-test name: k8s-user-test@kubernetes - context: cluster: kubernetes user: kubernetes-admin name: kubernetes-admin@kubernetes current-context: kubernetes-admin@kubernetes kind: Config preferences: {}users: - name: k8s-user-test user: client-certificate-data: REDACTED client-key-data: REDACTED - name: kubernetes-admin user: client-certificate-data: REDACTED client-key-data: REDACTED
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 [root@k8s - master-01 pki]# kubectl config use- context k8s- user - test@kubernetes #切换k8s- user - test这个用户,并使用get 获取pods资源信息to context "k8s-user-test@kubernetes". @k8s - master-01 pki]# kubectl get pods-7 fb7fd49b4-4 wdnq 1 / 1 Running 0 7 d3h-7 fb7fd49b4-6 mvlr 1 / 1 Running 0 7 d3h-7 fb7fd49b4-6 rbrv 1 / 1 Running 0 7 d3h-7 fb7fd49b4- jqsvj 1 / 1 Running 0 7 d3h-7 fb7fd49b4- r5mrl 1 / 1 Running 0 7 d3h
1 2 [root@k8s-master-01 pki]# kubectl get pods -n kube-system #测试获取kube-system这个名称空间的pods信息Error from server (Forbidden): pods is forbidden: User "k8s-user-test" cannot list resource "pods" in API group "" in the namespace "kube-system"
由于k8s-user-test账户不具备创建的权限,这也说明普通用户是无法进行创建K8S资源的,除非进行授权。如下,我们另开一个终端,将配置到一个普通用户yedong上,使其使用k8s-user-test账户进行通信
以下步骤在root权限下执行
1 2 3 4 [root@k8s -master-01 ~]# useradd yedong @k8s -master-01 ~]# cp -rp .kube/ /home/yedong/ @k8s -master-01 ~]# chown -R yedong.yedong /home/yedong/ @k8s -master-01 ~]# su - yedong
以下步骤在普通用户yedong下执行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 [yedong@k8s-master-01 ~]$ kubectl config use-context k8s-user-test@kubernetes Switched to context "k8s-user-test@kubernetes". [yedong@k8s-master-01 ~]$ kubectl config view apiVersion : v1 clusters : - cluster: certificate-authority-data : DATA+OMITTED server : https://172.16.50.200:6443 name : kubernetes contexts : - context: cluster : kubernetes user : k8s-user-test name : k8s-user-test@kubernetes - context: cluster : kubernetes user : kubernetes-admin name : kubernetes-admin@kubernetes current-context : k8s-user-test@kubernetes kind : Config preferences : {} users : - name: k8s-user-test user : client-certificate-data : REDACTED client-key-data : REDACTED - name: kubernetes-admin user : client-certificate-data : REDACTED client-key-data : REDACTED
以下步骤在root权限下执行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 [root@k8s-master -01 ~]ROLE AGE read -pods Role/pods-reader 16h master -01 ~]"ye-read-pods" deleted
以下步骤在普通用户yedong下执行
1 2 [yedong@k8s-master-01 ~]$ kubectl get pods #删除后,在yedong普通用户上进行获取pods资源信息,就立马出现forbidden了Error from server (Forbidden): pods is forbidden: User "k8s-user-test" cannot list resource "pods" in API group "" in the namespace "default"
clusterrole定义(User –> Clusterrolebinding –> Clusterrole) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 [root@k8s-master-01 pki] # kubectl config use-context kubernetes-admin@kubernetes #切换会kubernetes-admin用户"kubernetes-admin@kubernetes" .@k 8s-master-01 pki]# kubectl create clusterrole cluster-read --verb=get,list,watch --resource=pods -o yaml > clusterrole-demo.yaml@k 8s-master-01 pki]# vim clusterrole-demo.yaml #定义clusterrole和权限apiVersion : rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind : ClusterRolemetadata :creationTimestamp : "2021-12-16T09:50:01Z" name : cluster-readresourceVersion : "879450" uid : 0 effd7d6-2 ed3-4 fdb-be1e-da1ad65de097rules :apiGroups :"" resources :verbs :@k 8s-master-01 pki]# kubectl apply -f clusterrole-demo.yaml #创建clusterrole
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 [root@k8s-master-01 pki]# kubectl get clusterrole-12 -09 T03:05:01Z-12 -09 T03:05:01Z-12 -16 T09:53:29Z-12 -09 T03:05:01Z
clusterrolebinding定义 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 [root@k8s-master-01 pki ]root@k8s-master-01 pki ]apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: creationTimestamp: null name: ye-read-all-pods roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: cluster-read subjects: - apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: User name: k8s-user-test
1 2 [root@k8s-master -01 pki]read -all-pods created
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 [root@k8s-master -01 pki]ROLE AGE 7 d22h7 d22h7 d22hnode -bootstrapper 7 d22hread -all-pods ClusterRole/cluster-read 2m 41s
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 [root@k8s-master-01 pki]# kubectl describe clusterrolebinding ye-read-all -podsName : ye-read-all -podsnone >none >Kind : ClusterRoleName : cluster-readKind Name Namespace
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 [yedong@k8s-master-01 ~]$ kubectl get pods #角色绑定后在yedong终端上进行获取pods信息,已经不会出现forbidden了-7 fb7fd49b4-4 wdnq 1/1 Running 0 7d19h-7 fb7fd49b4-6 mvlr 1/1 Running 0 7d19h-7 fb7fd49b4-6 rbrv 1/1 Running 0 7d19h-7 fb7fd49b4-jqsvj 1/1 Running 0 7d19h-7 fb7fd49b4-r5mrl 1/1 Running 0 7d19h-01 ~]$ kubectl get pods -n kube-system #更换名称空间进行查看也是可行的-7568 f67dbd-bsnsh 1/1 Running 2 7d22h-7568 f67dbd-xjkmx 1/1 Running 2 7d22h-01 1/1 Running 10 (7d20h ago) 7d22h-01 1/1 Running 10 (7d20h ago) 7d22h-01 1/1 Running 0 22h-26466 1/1 Running 1 7d22h-4 qxhf 1/1 Running 2 7d22h-01 1/1 Running 0 22h-01 ~]$ kubectl delete pods nginx-7 fb7fd49b4-jqsvj #但是进行删除pod就无法进行,因为在授权时是没有delete权限的Error from server (Forbidden): pods "nginx-7 fb7fd49b4-jqsvj" is forbidden: User "k8s-user-test" cannot delete resource "pods" in API group "" in the namespace "default"
从上面的实验,我们可以知道对用户k8s-user-test进行集群角色绑定,用户k8s-user-test将会获取对集群内所有资源的对应权限。
User –> Rolebinding –> Clusterrole 将k8s-user-test通过rolebinding到集群角色cluster-read当中,此时,k8s-user-test仅作用于当前名称空间的所有pods资源的权限
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 [root@k8s-master -01 pki]"ye-read-all-pods" deletedmaster -01 pki]master -01 pki]read -podsread User name : k8s-user-testmaster -01 pki]read -pods createdmaster -01 ~]$ kubectl get pods7 fb7fd49b4-4 wdnq 1 /1 Running 0 7 d19h7 fb7fd49b4-6m vlr 1 /1 Running 0 7 d19h7 fb7fd49b4-6 rbrv 1 /1 Running 0 7 d19h7 fb7fd49b4-jqsvj 1 /1 Running 0 7 d19h7 fb7fd49b4-r5mrl 1 /1 Running 0 7 d19hmaster -01 pki]ROLE AGE read -pods ClusterRole/cluster-read 3m 4smaster -01 ~]$ kubectl get pods -n kube-systemUser "k8s-user-test " cannot list resource " pods" in API group " " in the namespace " kube-system"
删除用户 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 [root@k8s-master-01 pki ]apiVersion: v1 clusters: - cluster: certificate-authority-data: DATA+OMITTED server: https://172.16.50.200:6443 name: kubernetes contexts: - context: cluster: kubernetes user: k8s-user-test name: k8s-user-test@kubernetes - context: cluster: kubernetes user: kubernetes-admin name: kubernetes-admin@kubernetes current-context: kubernetes-admin@kubernetes kind: Config preferences: {}users: - name: k8s-user-test user: client-certificate-data: REDACTED client-key-data: REDACTED - name: kubernetes-admin user: client-certificate-data: REDACTED client-key-data: REDACTED
1 2 [root@k8s-master-01 pki]from /root/ .kube/config
1 2 [root@k8s-master -01 pki]Property "users.k8s-user-test" unset.
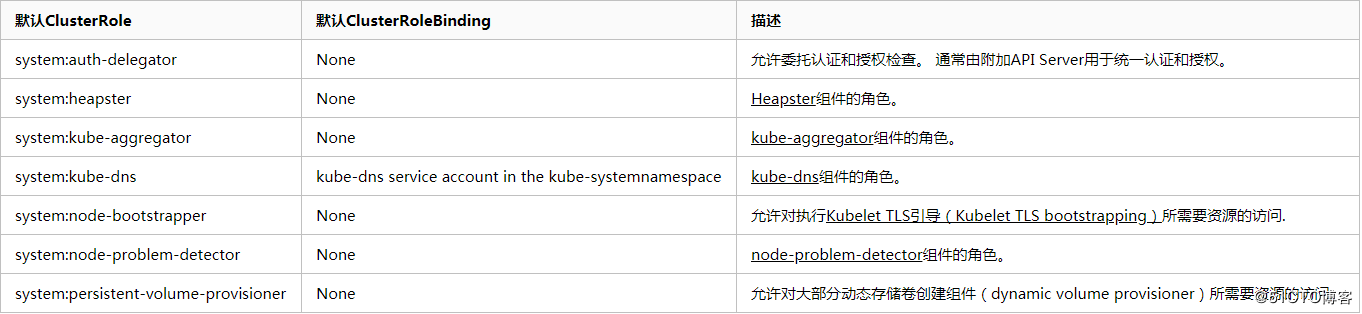
默认角色与默认角色绑定 API Server会创建一组默认的ClusterRole和ClusterRoleBinding对象。 这些默认对象中有许多包含system:前缀,表明这些资源由Kubernetes基础组件”拥有”。 对这些资源的修改可能导致非功能性集群(non-functional cluster)故障。一个例子是system:node ClusterRole对象。 这个角色定义了kubelets的权限。如果这个角色被修改,可能会导致kubelets无法正常工作。
所有默认的ClusterRole和ClusterRoleBinding对象都会被标记为kubernetes.io/bootstrapping=rbac-defaults。
自动协商 每次启动时,API Server都会更新默认ClusterRole所缺乏的各种权限,并更新默认ClusterRoleBinding所缺乏的各个角色绑定主体。 这种自动更新机制允许集群修复一些意外的修改。由于权限和角色绑定主体在新的Kubernetes释出版本中可能变化,这也能够保证角色和角色 绑定始终保持是最新的。
如果需要禁用自动更新,请将默认ClusterRole以及ClusterRoleBinding的rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate 设置成为false。 请注意,缺乏默认权限和角色绑定主体可能会导致非功能性集群问题。
当集群RBAC鉴权机制(RBAC Authorizer)处于开启状态时,则自动协商功能默认是被启用的。
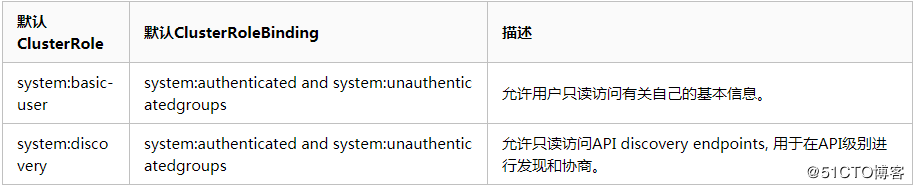
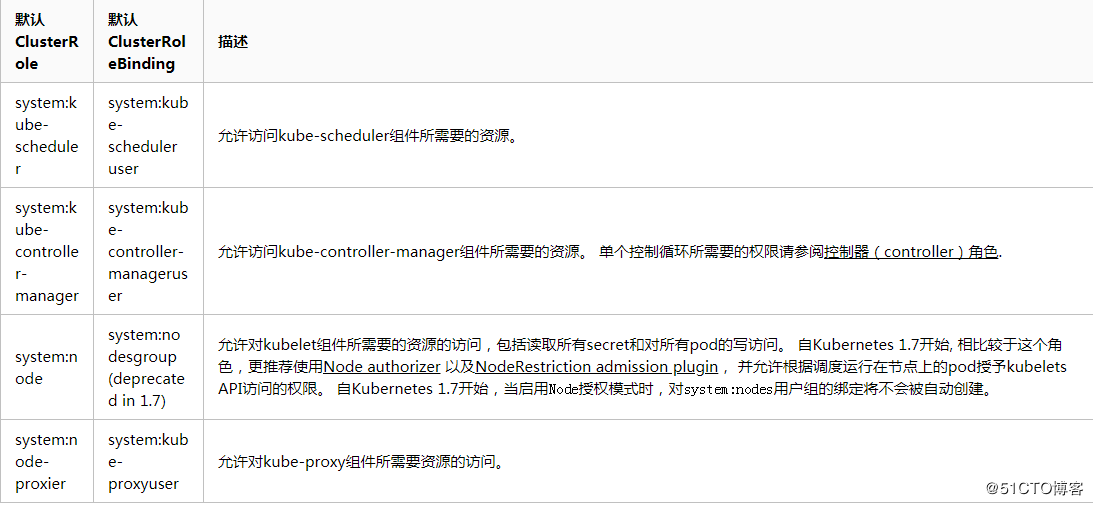
发现类角色 下面是一些默认Clusterrole绑定默认的Clusterrolebinding
面向用户的角色 一些默认角色并不包含system:前缀,它们是面向用户的角色。 这些角色包含超级用户角色(cluster-admin),即旨在利用ClusterRoleBinding(cluster-status)在集群范围内授权的角色, 以及那些使用RoleBinding(admin、edit和view)在特定命名空间中授权的角色。
核心组件角色
其它组件角色